Interesting Cat Facts (Senses)
by Michael
(London, UK)
Two useful tags. Click either to see the articles:- Toxic to cats | Dangers to cats
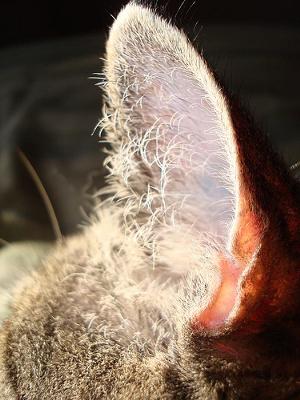
The super mobile cat ear - photo by Wombatunderground1 (Flickr)
A concise page of interesting cat facts to do with its senses. Although we are often not that aware of it, the domestic cat has amazing senses, sometimes many times more sensitive than ours.
This is not always the case, however. (Cat Anatomy)
Smells
- The sense of smell is the first of the cat's senses that is developed. The new born kitten smells the aroma of mother's mammary glands at birth. Within a couple of days the kitten reacts to offensive smells.
- The part of a cat's brain that is dedicated to analyzing odours (olfactory bulb) has 67 million cells, which is 15 million more than for humans. The dog is in a league of its own though with a sense of smell 100,000 times more sensitive than ours.
- Young kittens removed from their litter mates will automatically crawl back towards the smell of its "home" and then fall asleep.
- Cats and dogs have a special organ between nose and mouth. A cat inhales air to pass over this organ. Hence the familiar grin a cat makes coupled with a concentrated facial expression.
- The smell of nutmeg makes a cat less bored it is said.
- Cats prefer environments where there are lots of smells. This is said to alleviate boredom.
Sounds
- Cats have more than twenty muscles in their ear flaps (pinnae - outer part of the ears). As we know the ears move independently of each other. The cat's body can move in one direction while the ears move in another direction.
- Cats are good at pinpointing the source of sound which serves their hunting skills. They can differentiate between sources of sound 8 centimetres apart from one metre away.
- Cats possess senses that are at the top end of all animal skills in detecting range of sounds (range of frequencies). The cat can hear over 10.5 octaves (human: 8 octaves) and frequencies from 35 kilohertz to 250 kilohertz. They can detect ultrasonic sound (sound with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing - greater than 20 kHz) produced by rodents.
- The cat is very adept at distinguishing the sounds made by other animals e.g. mouse and shrew.
- When a cat senses our arrival in our car before seeing us, it is said that they are in fact hearing the ultra high frequency sounds made by the car well before it is seen or heard by us.
Sight
- A cat's sight has evolved to support its other senses to make it a top predator.
- The cat's pupil (opening) is elliptical (squashed circle) allowing it to see under a wider range of light conditions. This wide range is enhanced by the fact the eyelid acts a shutter going down over the pupil which results in a smaller amount of light entering the eye.
- It is said that cats' eyes have several focal points allowing for sharp images in low light.
- Strange though it sounds, it is also said that a cat's eyes change according to the course of the sun.
- Siamese cats have a squint because it is an attempt to correct double vision caused by a genetic defect affecting optical nerves and brain.
- Cats have excellent peripheral vision (vision outside the center). This allows a cat to apparently stare into space while looking at things on either side of center vision.
- The cat family is considered to have the best binocular vision (two eyes working together to form a single image and to provide distance judgments). This is because the eyes are placed at the front and high up on the skull.
- It is claimed by some that domestic cats are a bit near sighted (can't see far away objects). Feral cats are long sighted (can't see close objects). I am not sure this is correct, however!
- Cats have a blind spit just like us. It is "under their nose". Cats sometimes have trouble seeing food close by and on the floor.
- Cats see colour but it is less saturated. They can see blue and green and "possibly red".
- The cat's third eyelid acts like a windscreen wiper. It is not usually visible. It can be seen if it is inflammed (cherry eye).
Touch
- A cat's whiskers are special. The are very sensitive and are able to pick up air currents. They are on their front paws as well as the face. The assist in killing prey and in night "vision".
- Cats are generally left pawed. 20% favour their right paw, 38% favour their left and 42 are ambidextrous (use both equally).
- Cats don't feel that something is painfully hot until it reaches 52 degrees centigrade while humans reach that point at 44 degrees centigrade.
- As well as for grooming, cats lick their fur to cool down as it acts like sweat (perspiration), utilising the latent heat of evaporation (of the saliva).
![]()
